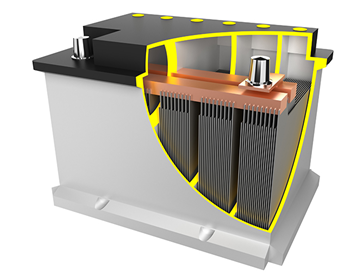
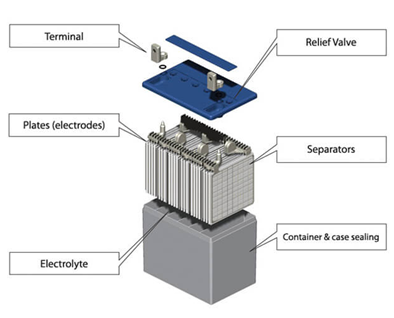
Within the unassuming shell of a lead-acid battery lies a complex and meticulously designed ensemble of components, each with a specific role to play in the storage and release of electrical energy. From the sturdy battery case that serves as its protective armor to the positive and negative plates responsible for energy storage, and the sulfuric acid-based electrolyte facilitating the essential chemical reactions, the lead-acid battery is a marvel of engineering.
As we embark on a journey to dissect and understand the key components that power our vehicles, backup systems, and countless other applications, we unveil the intricate dance of chemistry and mechanics that make lead-acid batteries an enduring and reliable choice in the world of energy storage.
Following are the components of a Lead Acid Battery
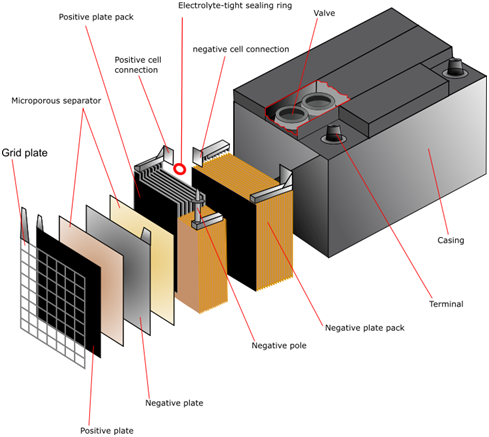
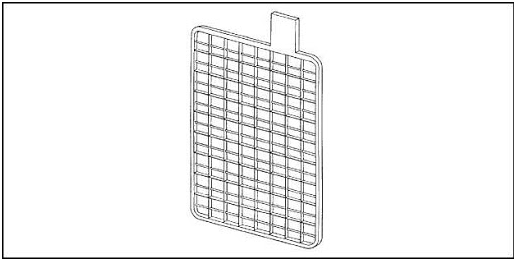
1. Battery Case: The battery case is like a sturdy shell that protects the internal components from damage and provides structural support.
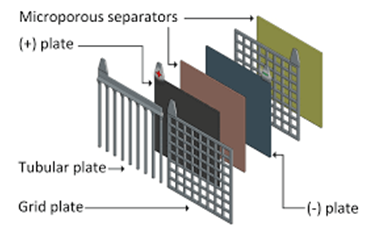
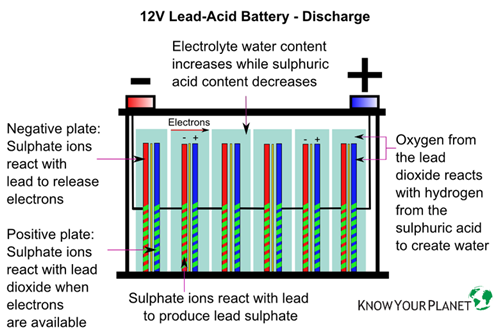
2. Positive and Negative Plates: These plates are the main energy-storing components of the battery. The positive plate is made of lead dioxide (PbO2), while the negative plate is made of pure lead (Pb). They react with the electrolyte to generate electrical energy.
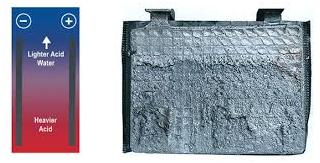
3. Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a mixture of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and water (H2O). It facilitates the chemical reactions between the plates, allowing the battery to store and release electrical energy.
4. Separator: The separator is a porous material placed between the positive and negative plates. It prevents direct contact between the plates while allowing the flow of ions, enabling the movement of charge during the battery’s operation.
5. Terminal Posts: These are the connection points on the battery that allow for the transfer of electrical energy to external devices. They are typically made of metal and provide a secure connection.
6. Vent Caps: The vent caps are small openings on the battery case that allow the release of gases produced during the charging and discharging processes. They help maintain the optimal pressure inside the battery.
7. Handle: Some batteries come with handles for easy transportation and installation. They provide a convenient way to carry the battery and ensure a secure grip.
8. Battery Terminals: These are the metal connectors located on the battery’s top surface. They provide the electrical connection points for external devices or circuits.
9. Battery Grids: The grids are the supporting structures for the positive and negative plates. They are typically made of lead or lead alloy and help maintain the shape and integrity of the plates.
10. Battery Separator Envelopes: Some lead-acid batteries have separator envelopes made of glass mats or absorbent fiberglass material. These envelopes hold the electrolyte and prevent spills during battery operation.
11. Battery Insulation: Insulation materials, such as rubber or plastic, are used to cover and protect the battery terminals, preventing accidental short circuits.
12. Battery Plate Coating: The plates of a lead-acid battery are often coated with various materials to enhance their performance and longevity. These coatings can include lead oxide, lead sulfate, or other additives that improve the battery’s efficiency and resistance to degradation.
The additional components work together to create a reliable and efficient lead-acid battery.
When it comes to lead-acid battery manufacturers in India, one notable company is Sarex. Sarex is a prominent battery manufacturer based in Aligarh, India. We specialize in producing high-quality lead-acid batteries for various applications. As a trusted battery manufacturer in Aligarh, Sarex focuses on delivering reliable and durable batteries that meet the needs of its customers. Our expertise and commitment to quality make them a key player in the battery industry in India. If you’re looking for a reliable battery, Sarex is worth considering.